EDITORIAL
CLINICAL MEDICINE. REVIEWS
The uterine fibroid, also known as the leiomyoma, according to the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, is a benign tumor commonly diagnosed among women of reproductive age. Pregnancy accompanied by uterine fibroids is a complex
case requiring special treatment and competencies from an obstetrician-gynecologist. The present scientific publications analysis reveals leiomyoma influence on pregnancy outcomes. The authors discuss the following obstetric complications related to uterine fibroids: miscarriages, premature birth, malposition, placental abruption, and post-partum complications.
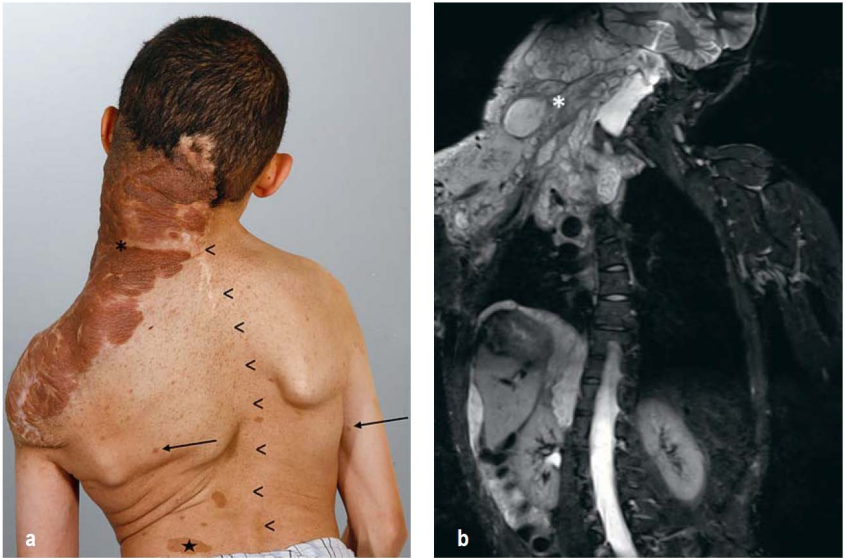
The paper analyzes the following modern approaches to neurofibromatosis visualization: magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, positron emission computed tomography, ultrasound scanning, and others. The article considers the role of radiological examination methods in medical screening, clinical course monitoring and therapy efficacy evaluation. Localized magnetic resonance imaging with contrast agents is the superior visualization technique for neurofibromatosis. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging is effective for screening of asymptomatic tumors and total tumor mass calculation, while positron emission tomography is used to reliably diagnose malignant transformations of neurofibromas. Computed tomography is also beneficial in bone alternation detection and surgery planning where it is used as an addition to magnetic resonance imaging data. Ultrasound scanning is applicable for superficial tumor observation. Comparative analysis of scientific literature proves the key role of comprehensive use of diverse radiological examination methods in prompt neurofibromatosis diagnostics and screening, patients monitoring and therapy results evaluation.
CLINICAL MEDICINE. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
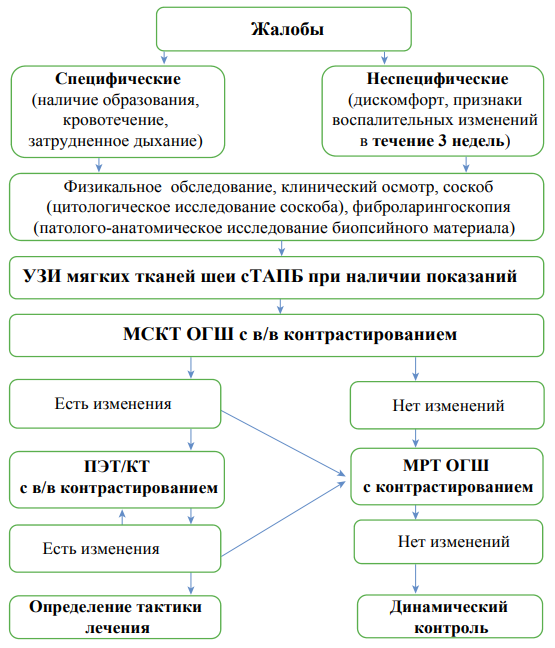
The paper presents a patient examination algorithm with the aim of oropharyngeal area tumor detection and differential diagnostics during initial consultation. This article illustrates the capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging, multislice and positron emission computed tomography in diagnosing, based on radiological evidence, the most common tumors affecting the oropharyngeal region.
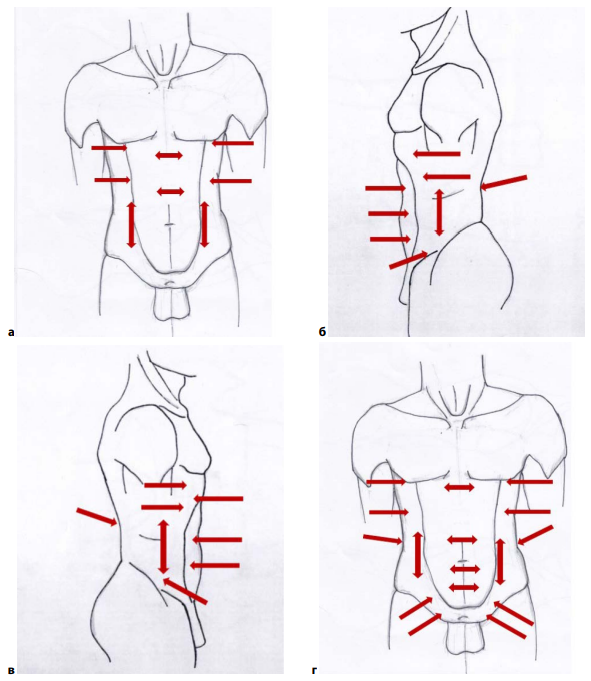
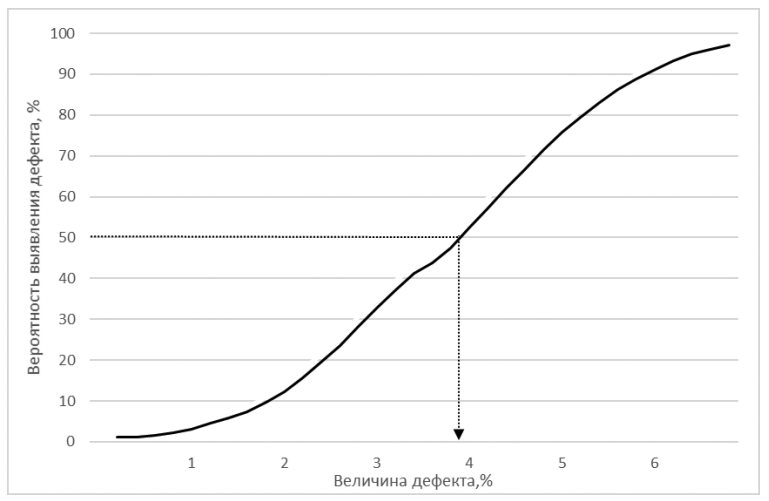
The study aims to assess the possibilities of ultrasound investigation for the best planning of surgical access in complicated necrotizing pancreatitis. Due to the high mortality (13.1–21.3%) and injuries during open surgeries, the treatment of acute pancreatitis still remains an urgent challenge. The results of 210 necrotizing pancreatitis cases of moderate and severe course are analyzed. The cases are divided into four types. The central type (model 1) is identified in 73 cases (34.8%), the left type (2) is in 65 cases (31%), the right type (3) is in 24 cases (11.4%), and the mixed type (4) is in 48 cases (22.8%). The ultrasound investigation, as the most affordable and informative method of diagnostics, was performed daily or every other day on-demand. A stepwise algorithm for investigating tissue planes was developed. The factors affecting the course of the disease in all four types are formulated. These include limitless spread of parapancreatitis, complex cavity configuration, and massive sequestration predominantly in the left, right, and mixed types (p = 0.0001), and the absence of an “acoustic window” for percutaneous drainage in the right and mixed types (p = 0.027). Minimally invasive surgical procedures, including percutaneous drainage, bougienage along the drains, and videoscopic necrosequestrectomy, were more frequently used in the central and left types. Open surgery is predominantly used in the right and mixed types (p = 0.0001). The optimal approach for adequate surgical treatment is determined by stepwise visualization of the tissue planes, taking into account the configuration and echosemiotics of fluid and necrotic accumulations, with justification for percutaneous drainage under ultrasound guidance. Thus, dynamic ultrasound investigation allows predicting the effectiveness of various surgical treatment methods, including minimally invasive ones, considering the best surgical access, which reduces mortality and improves treatment outcomes in complicated necrotizing pancreatitis
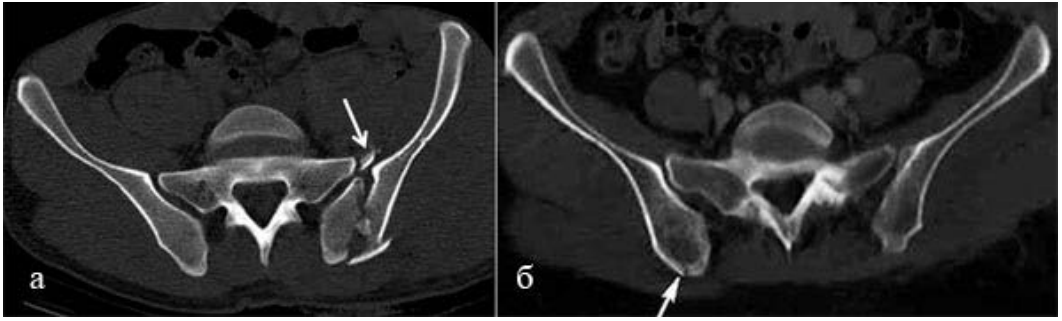
The paper focuses on child pelvic fractures occurring in up to 5% of the polytrauma injured. The aforementioned traumas differ from adult pelvic fractures and require a specific therapeutic approach. At present, there is no consensus on the priority of one of the following visualization types: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. The order of diagnosing a pelvis injury in child polytrauma cases is also debatable. The article presents the pelvic trauma diagnostic capabilities of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging among children with polytrauma. A cohort of 187 pediatric patients with pelvic injuries and polytrauma (mean age, 13.5 years) is investigated. Multislice computed tomography using a 128-slice “Ingenuity Elite 128” (Philips) scanner is performed on all patients. The 3T scanner magnetic resonance imaging is conducted on 21 children, and fat suppressed 3D versions of multiplanar STIR, T1-, T2-, and PD weighted images are obtained. Injury severity score (ISS) of the 187 children varied from 26.47 to 28.1 points with the average range
of 26.11±1.5. The 72.72% (n = 136) of the pelvic fractures are multiple, 21.39% (n = 40) are complex, 23.52% (n = 44) are unstable. Among 69 patients diagnosed with anterior pelvic ring injury according to computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging has found 68.11% (n = 47) cases of comorbid posterior pelvic ring fractures. Computed tomography conduction on children with suspected pelvic injuries are obligatory for polytrauma instances. While magnetic resonance imaging has a high sensitivity diagnosing all non-muscular and pelvis injury types, computed tomography is preferable in specified cases due to its operation speed and metal stabilizers.
LIFE SCIENCES. REVIEWS
The study analyzes vaping spread and comprehensive effect of electronic cigarette smoking on lung morphology and function. Materials confirm a high percentage of young people aged 13–17 vaping, which determines the need for promoting awareness about its potential harm and subsequent adverse medical consequences among children. The specified electronic cigarette content is given, showing its type diversity. The article describes the damaging effect of various vaping product components, defining several nociinfluence
mechanisms on the respiratory system. The analysis of scientific publications on the topic is conducted using Web of Science, Scopus, MEDLINE, PubMed, and eLIBRARY.RU databases with a search depth of 10 years. This paper presents statistical measures and clinical case studies, indicating a connection of vaping with obliterative bronchiolitis. This paper presents new diagnostic techniques that prove vaping use-associated pulmonary injury. The authors consider therapy issues, the difficulty of which lies in the absence of standardized therapeutic approaches at present. Examining this disease is significant for identifying its specific manifestations and developing therapeutic modalities.
LIFE SCIENCES. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
The article presents results of the scientific research on the analytical characteristics study of Russian multiparameter control materials “BIOCONTROL” for biochemical tests using human blood serum. The paper proves the control materials “BIOCONTROL” compliance with the Russian requirements documents on ruggedness control in intra-laboratory quality evaluation procedures. The authors compare the findings collected from the following four analytical systems: BioMajesty JCA-BM6070/C (Jeol Ltd), BS-2000 (Mindray Ltd), Cobas 8000 (Roche Diagnostics), and Olympus AU 2700 (Beckman Coulter). The study reveals that the control materials “BIOCONTROL” meet the established reproducibility standards of results within one and multiple analytical runs on the tested techniques majority. The developed evaluation mechanism confirms the control materials’ versatility in use with different analytical systems. This fact makes it possible to create experimental groups in results inter-laboratory comparison procedures. The opportunity to compare analytical characteristics of the in vitro diagnostics medical devices for checking their accordance with the intended function leads to laboratory tests quality improvement and mitigation of the risks associated with Russian patients’ safety.
The paper demonstrates photoplethysmography diagnostics results of the university students’ cardiovascular system functional state. Such parameters as pulse wave type, vascular stiffness (alkaline phosphate, Alp, %), and physiological vascular age (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, AGI, age) are considered cardiovascular risk factors and examined in this article. The experimental data is analyzed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, the difference significance is defined based on the Student’s t-test. The Student’s t-test is also applied in the significant response differences representation of the studied parameters assessment results as an average standardized deviation. The author takes the value р ≤ 0.05 as the critical significance level while analyzing statistical hypotheses. The conducted research results allow diagnosing combined types of pulse waves (АВС and ВС) among 43.37% of the students in varied percentage ratio, indicating the developing artery structure alternation. The theory is proved by the 28.3% of photoplethysmograms with high frequency and amplitude of the pulse waves testifying enhanced arterial stiffness. The specified factor reveals the following statistically significant gender differences: male arterial stiffness (Alp = –9.35 ± 0.47) is 1.24 times higher than the female one (Alp = –11.64 ± 0.65). Assessment of physiological vascular age of the examined shows sufficiently high values considerably exceeding the actual age (AGI = 30.89 ± 1.04 years). According to this parameter, the physiological vascular age corresponds to the actual age only in 9.44% of the cases. The factor analysis shows the absence of statistically significant gender differences, while the deviations from the age norm (12.07 ± 0.91 years among females and credibly higher among males being 20.31 ± 0.12 years) appear statistically significant (р < 0.05). Most of the tested students have vascular alternations indicated mainly by the AGI measure. It is assumed that researchers can use the assessment of physiological vascular age, stiffness, and pulse wave type in cardiovascular risks diagnostics and development of cardiovascular disease induction remedies.
LIFF SCIENCES. CLINICAL CASE
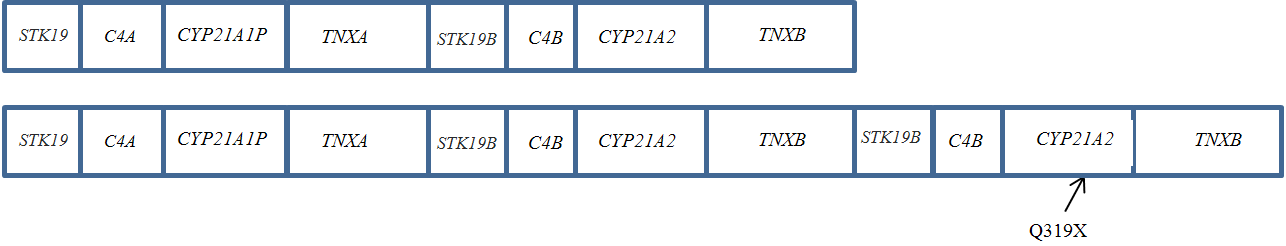
The article describes a case of prenatal molecular genetic testing performed at 11 weeks and 2 days of gestation in a family that includes a proband who has a salt-wasting form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. The authors aim to conduct a molecular prenatal study based on the proband’s identified pathogenic variants in the gene CYP21A2 as part of genetic counseling given the 25% potential risk of giving birth to a neonate with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. As a result, the molecular genetic testing reveals the following pathogenic variants in the gene CYP21A2: R357W (rs7769409) and Q319X (rs7755898) in a heterozygous state. The analysis of pathogenic variant inheritance confirms that the risk of the fetus having congenital adrenal hyperplasia is minimal.
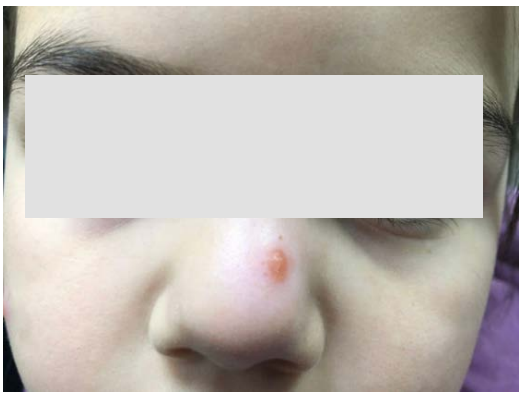
The aim of the study is to provide dermatovenerologists, infectologists, and other medical workers with relevant information about cutaneous leishmaniasis as well as to present a cutaneous leishmaniasis case. The authors perform a retrospective analysis of original medical records and photo archives related to the cutaneous leishmaniasis case treated at the “Surgut Clinical Dermatovenerologic Dispensary”, Surgut. Local dermatovenerologists have diagnosed a cutaneous form of the specified disease, while it is atypical for the North of Russia. The patient has consulted the infectious disease specialist promptly for follow-up examination and medical treatment. Cutaneous leishmaniasis is an urgent interdisciplinary problem requiring close attention from dermatovenerologists, infectologists, and epidemiologists. The growing number of introduced cases, diagnostic complexity, and limited therapeutic methods determine the necessity of raising awareness about this disease among medical workers, improving comprehensive interaction, and advancing the laboratory facilities for timely pathology detection.