EDITORIAL
CLINICAL MEDICINE. REVIEWS
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory recurrent skin disease accompanied by pruritus. The global prevalence of atopic dermatitis has spurred increased medical interest in optimizing treatment strategies, discerning the need for basic versus genetically engineered therapies. Doctors pay much attention to diseases caused by the deterioration of the body’s resources, but they must have maximum information about the patient’s near and distant future. Knowledge of individual cases, including evaluation of the results of different treatment methods, allows to classify patients into high- or low-risk groups and to choose the necessary treatment tactics.
This article reviews the world literature with a search depth of 5 years in the following databases: eLIBRARY.RU, PubMed, Wiley, Google Scholar. This review examines articles on diagnosing and controlling the course of atopic dermatitis. New methods of controlling the course of the disease are being developed in this regard.
The purpose is to substantiate the characteristics, develop a data set for testing and monitoring the quality of artificial intelligence (AI) services for prostate morphometry on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results. We carried out a search of scientific literature in PubMed and RINC databases with the search depth, mostly not exceeding 10 years. In the structure of malignant neoplasm morbidity among the male population, tumors steadily rank first in Russia and second in the global perspective. In Russia in 2013, the corresponding morbidity was 34.62 cases per 100 thousand people, and in 2023, it increased to 50.33 cases. There is a steady annual increase in the absolute number of first-time diagnoses of prostate cancer. There was a certain decline in this indicator during the COVID-19 pandemic, but now the growth has restarted. This type of pathology ranks third (9.0%) in the structure of mortality from malignant neoplasms among the male population. MRI has a special role in screening and diagnosis of prostate diseases. The varying levels of doctors’ competence and the labor-intensive processing, interpretation, and measurements often limit the implementation of MRI, because of the time needed to describe the research results. Computer vision technologies can serve as one of the potential ways of solving this problem. Both the lack of data itself and defects in data markup limit the introduction of AI technologies in practical healthcare.
Closed chest injury traditionally takes a leading position both among all injuries and among the causes of mortality. The article analyses the scientific literature of Russian and foreign authors regarding the treatment of thoracic injury, emphasizing surgical methods for stabilizing the chest wall with multiple rib fractures. We used the electronic information resources eLIBRARY.RU and PubMed, primarily searching the last 10 years.
Since the early 1900s, practitioners have used surgical methods to fix multiple rib fractures, and these methods have grown increasingly popular in recent decades. The possibilities of surgical chest wall stabilization in th treatment of patients with multiple rib fractures have improved with the development of the osteosynthesis industry and the emergence of new technologies. The variety of surgical methods for multiple rib fractures treatment emphasizes both the demand for solving this problem and surgeons’ dissatisfaction with the treatment results of the proposed methods. Further research into the topical issues surrounding surgical rib cage stabilization is needed to elevate the quality of specialized care for patients with thoracic injuries.
The purpose of this review is to compile current literature data on the unique immunological properties and regenerative capabilities of breast milk. This review considers the immature cellular and humoral immune response of newborns and infants, and the ability of breast milk components to compensate for this immaturity. Microchimerism caused by breastfeeding is under discussion in the specialized literature and plays a key role in the formation of the immune system and the child’s organism. Milk stem cells integrate and differentiate into the tissues of the newborn. Breast milk of a nursing woman is the richest source of oligosaccharides, the numerous positive effects of which contribute to the formation of a proper intestinal microbiome and a protective intestinal barrier. Nutrient transport is mediated by exosomes synthesized by mammary gland and breast milk cells. Many researchers consider exosomes as a potential means of targeted drug delivery. One of especially interesting features is the HAMLET protein complex, which has anti carcinogenic effects.
The analysis included scientific publications indexed in Web of Science Core Collection databases and thematic publications in scientific journals included in RSCI, with a search depth of mainly 10 years.
CLINICAL MEDICINE. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
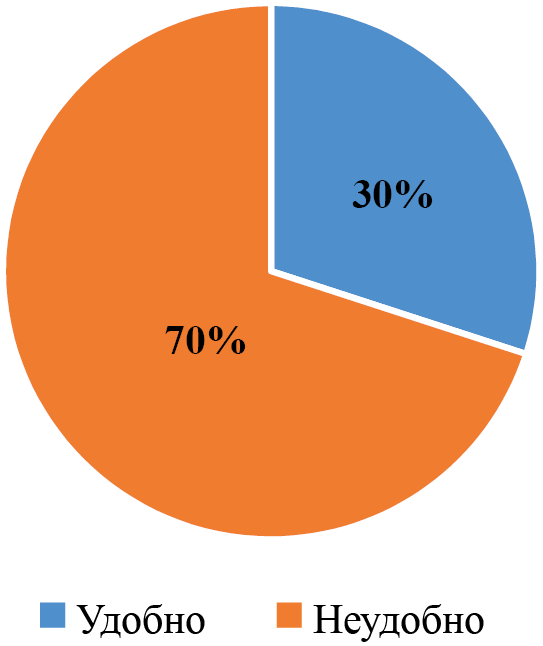
article details a portable multifunctional ultrasound device’s results from its testing period in 2024, used by a mobile medical team at the Surgut City Clinical Emergency Medical Center. This study found that ultrasound examinations are not significantly needed for patients before hospital arrival. The collected data can support future discussions about the effectiveness of ultrasound diagnostics in emergency care and optimizing treatment.
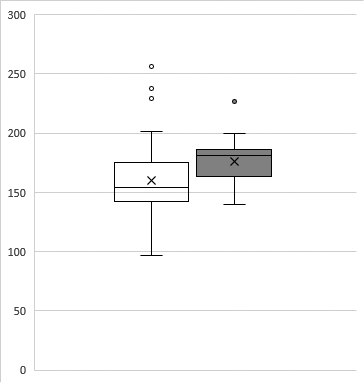
We studied the diagnostic and prognostic significance of fructosamine and 1,5-anhydroglucitol levels in peripheral blood during pregnancy complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus. Analysis demonstrated the absence of significant differences in marker levels relative to glycated hemoglobin and fasting plasma glucose levels in the presence of mild iron deficiency anemia. Higher fructosamine levels in the third trimester were associated with fetal macrosomia.
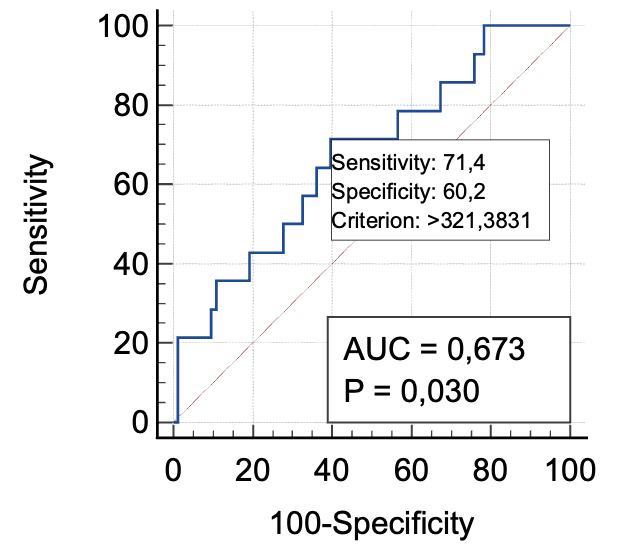
Breast cancer remains one of the widespread diseases in female population. Surgical method is the basic approach to cytoreduction at the early stage of disease diagnostics, ensuring the achievement of higher rates of distant relapse-free and overall survival. However, surgical complications remain an acute concern. Performing preserving surgeries with biopsy of the sentinel lymph node in the postoperative period can lead to the development of hematoma, seroma, infection, and flap necrosis. The developed method of breast resection with lymph node dissection significantly reduced early postoperative complications by 3.8% (against 27.6% with standard incision, p <0.05). Inflammatory infiltrate in the postoperative wound area occurred in 1.9% of patients (compared to 11.4% with the standard incision, p < 0.05), and seroma in the postoperative wound area occurred in 1.9% of patients (compared to 14.2% with the standard incision, p < 0.05). We successfully tested our proposed method for predicting early postoperative complications, and it showed prognostic value. The main predictor of the onset of wound complications was the index of microcirculation. Thermometry was an additional method. Thus, the use of Z-shaped incision for breast cancer preserving surgery, as well as the use of screening techniques, is important for prognosis optimization of early surgical complications.
This work evaluates the effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in treating diffuse peritonitis. The treatment results of 130 patients with acute surgical pathology of abdominal cavity organs complicated by secondary diffuse peritonitis were analyzed by the authors. The authors evaluated postoperative lethality, morbidity, and the severity of postoperative complications, and analyzed the relaparotomies. Two groups of patients are analyzed. The main group (90 patients) received traditional debridement, while the control group (40 patients) received photodynamic therapy at the operation’s final stage. Postoperative lethality in the main group was statistically lower than in the control group (17.5% compared to 35.5%). Severe postoperative complications occurred in 3 patients in the main group (7.5%) and in 24 patients in the control group (26.6%). The analysis of relaparotomies revealed that the necessity to perform two or more relaparotomies in the main group amounted to 30% versus 53.3% in the control group. Photodynamic therapy included in the program of surgical treatment of patients with generalized secondary purulent peritonitis and sepsis has a significant antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, which is indicated by a statistically faster relief of peritonitis clinical manifestations. The use of photodynamic therapy allows to reduce the severity of postoperative complications and lethality, which permits recommending it for clinical use.
CLINICAL MEDICINE. CLINICAL CASE
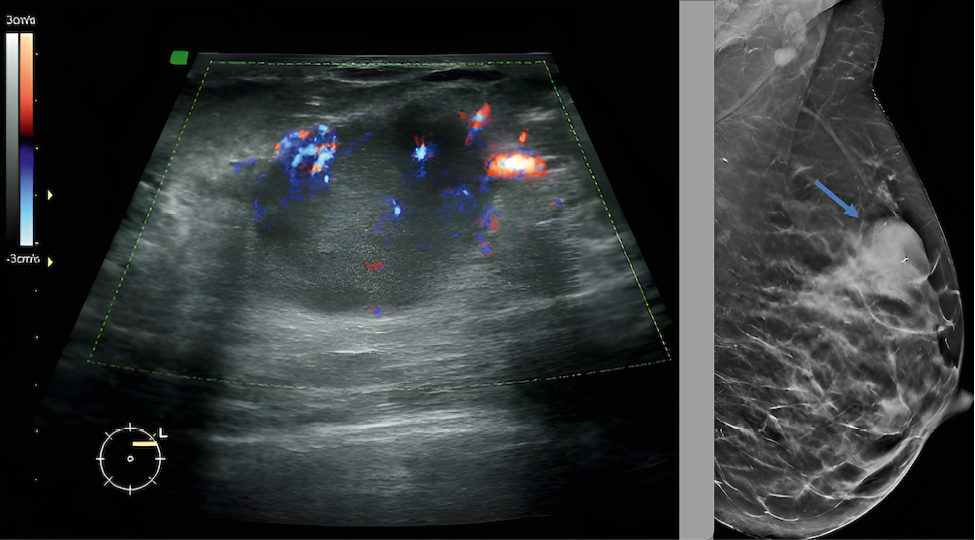
The article examines the diagnostics of pregnancy associated breast cancer. There is an increase in the morbidity of breast cancer among women of reproductive age, which is associated with a later age of childbearing. Pregnancy complicates diagnostics due to physiologic and hormonal changes in the mammary gland. Main diagnostic methods include ultrasound investigation and biopsy. This study presents clinical cases to demonstrate the importance of early detection and a comprehensive treatment approach. Treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach considering both maternal and fetal health.
LIFE SCIENCES. REVIEWS
The aim is to systematize the literature on the effectiveness of energy metabolism drug regulators
in medical practice. A systematic review of the scientific literature is conducted using CyberLeninka and eLIBRARY.RU, PubMed, etc. databases. The search primarily covered a 10-year period, including foundational research. Drugs optimizing energy processes, in particular those containing succinic acid, contribute to more efficient functioning of the organism under conditions of increased workload and stress. These processes enhance the body’s capacity to adapt to adverse conditions, improving its self-regulatory functions and maintenance of homeostasis. These drugs can also play an important role in the prevention and treatment of various diseases associated with several imbalances in the body. Improving factors affecting the body’s tolerance significantly boost well-being and quality of life.
LIFE SCIENCES. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
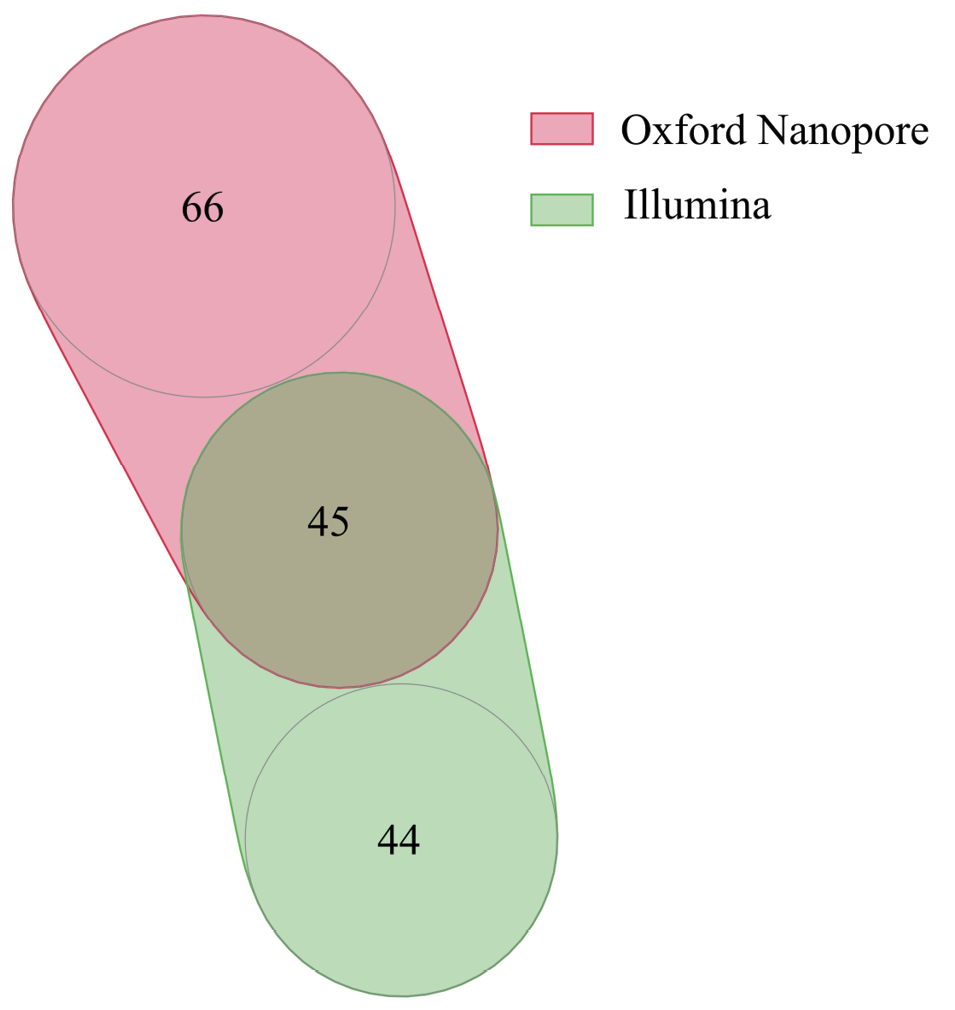
The use of modern sequencing methods enables us to determine the taxonomic biodiversity of various bacterial communities. Specifically, it allows to assess the diversity of bacterial strains that are not cultured. At present, there are two generations of sequencing technologies that enable the determination of microbial community diversity: 2nd generation (represented by Illumina and BGI) and 3rd generation (Nanopore and PacBio). However, as these technologies use different approaches to sequencing, there is a question of reproducibility of the results. This research revealed that using Illumina and Nanopore sequencing methods differs in terms of diversity indices and taxonomic diversity. This data emphasizes the requirement to develop advanced methods for sample preparation and DNA sequencing to achieve an unequivocal microbial community profile.